Stakeholder Engagement Process in 6 Steps

Find out what stakeholder engagement means and what the implementation process looks like in six key steps.
Companies have always practiced stakeholder engagement but in a limited way. Be it customer feedback, focus groups for product development, or shareholder inputs, it is all a form of stakeholder engagement. What has changed is the variety and number of stakeholder groups whose input is considered significant to the corporate decision-making process.
Seen through the lens of sustainability, stakeholder engagement falls under the social aspect (the S in ESG). It encapsulates the impact that the workings of a business have on people, be it its employees, investors, or affected communities.
In this article, we take a comprehensive look at who a stakeholder is, what stakeholder engagement means, and what it actually looks like when implemented.
- Who is a stakeholder?
- What is Stakeholder Engagement?
- 6 Key Steps of Stakeholder Engagement
- Related Post
Who is a stakeholder?
Stakeholders are individuals, groups, or organizations that can influence or are impacted by a business’s operations. They include those who have a vested interest in the company’s workings, products, services, and decision-making processes. It is important to note that stakeholders do not include the general public, but rather specific parties with a direct stake in the organization.
Stakeholders can be internal and external to the organization. Common examples of stakeholders include investors, suppliers, shareholders, consumers, employees, volunteers, government entities, and relevant local communities. These stakeholders play significant roles in the success and sustainability of the business. They contribute resources, rely on the company’s offerings, and are affected by its actions and decisions.
What is Stakeholder Engagement?
At its core, stakeholder engagement involves establishing communication and participation with all stakeholders. However, practical implementation involves considering multiple variables.
- The company must first determine its goals for engagement, whether it is process-centric, specific to certain operations, or more wide-ranging. The duration of engagement also needs consideration, whether it is a one-time occurrence, a short-term, or a long-term ongoing process.
- Next, the company must identify the relevant stakeholders and prioritize those who are most affected or influenced. This step helps the company focus its efforts on engaging with those who have the greatest stake in its operations and decisions. By understanding the specific needs and concerns of these stakeholders, the company can tailor its engagement strategies to address their interests effectively. This targeted approach enhances the relevance and impact of stakeholder engagement initiatives.
- With consideration for available resources, the company can then establish processes and systems to ensure effective stakeholder engagement. It must allocate appropriate resources, such as personnel, time, and budget, to support meaningful interactions and feedback mechanisms.
By designing frameworks that facilitate open and transparent communication, the company can foster constructive dialogue, build trust, and gather valuable insights from stakeholders. These processes and systems should be implemented with careful planning and monitoring to ensure that stakeholder engagement efforts are efficient, impactful, and aligned with the company’s overall objectives.

6 Key Steps of Stakeholder Engagement
1. Stakeholder Identification
When seeking engagement, it is important to identify all those affected, influenced, or capable of affecting or influencing operations. A comprehensive view must be taken to accurately portray the stakeholder landscape. This ensures a thorough understanding and provides a fuller picture of the stakeholders involved.
By considering the broader context and taking a comprehensive approach, businesses can identify stakeholders beyond the obvious ones. This includes those directly impacted as well as those with indirect or potential influence. Taking this comprehensive view also enables businesses to understand interconnected relationships, anticipate impacts, and develop effective strategies.
What stakeholder identification looks like in practice
- Brainstorming
- Listing by organization, geographical area, and involvement
- Listing those affected (positively or negatively)
The result is a comprehensive list of all stakeholders with details such as contact information, organization, group, titles, and other relevant information that might be needed for later communication.
“When your business prioritizes the wellbeing of all of its stakeholders, then all of those stakeholders gain respect for the business and your business can utilize that respect as a sort of currency and a means to accomplish business objectives. “
Hendrith Vanlon Smith Jr, CEO of Mayflower-Plymouth
2. Stakeholder Analysis
The identification data is then analyzed and categorized into groups and subdivisions using various parameters, including their level of effect, influence, expertise, and more. These categories are tailored based on the nature and objective of the engagement process. Through analysis, stakeholders are organized into specific groups that align with the goals and purpose of the engagement initiative. This categorization enables businesses to prioritize their efforts and tailor engagement strategies accordingly.
By understanding the unique characteristics and needs of each stakeholder group, organizations can develop targeted approaches that effectively address their interests and concerns.
An efficiently executed stakeholder analysis:
- Allows for a better understanding of the stakeholder groups
- Development of a more effective engagement strategy and plan
- Better communication with stakeholders
- Understanding the scale of the engagement project in terms of work hours, cost, etc.
Stakeholder expectations
Identifying: Once prioritization has been done, stakeholder needs, motivations, and expectations can be explored in order of priority.
Manage: This is key for project-based stakeholder engagement and caters to managing stakeholder expectations for the duration of the project. But to some degree stakeholder expectations management is also relevant for overall engagement purposes, for example, with regard to suppliers, the organization can use stakeholder engagement to know in advance the expectations of its suppliers, thereby helping it plan better and be more resilient to any change
3. Stakeholder Mapping
Mapping entails taking the data from the previous processes and representing it via a map. Mapping provides a comprehensive visual overview of:
- Stakeholder groups with levels of influence and effect
- Relationship between stakeholder groups, and the
- Nature of those relationships (how they are connected to each other).
Benefits of Stakeholder Mapping
- Assistance with prioritizing stakeholders
- Shows interest and influence
- Helps bring clarity by providing a visual overview
- Drives more effective engagement strategy development
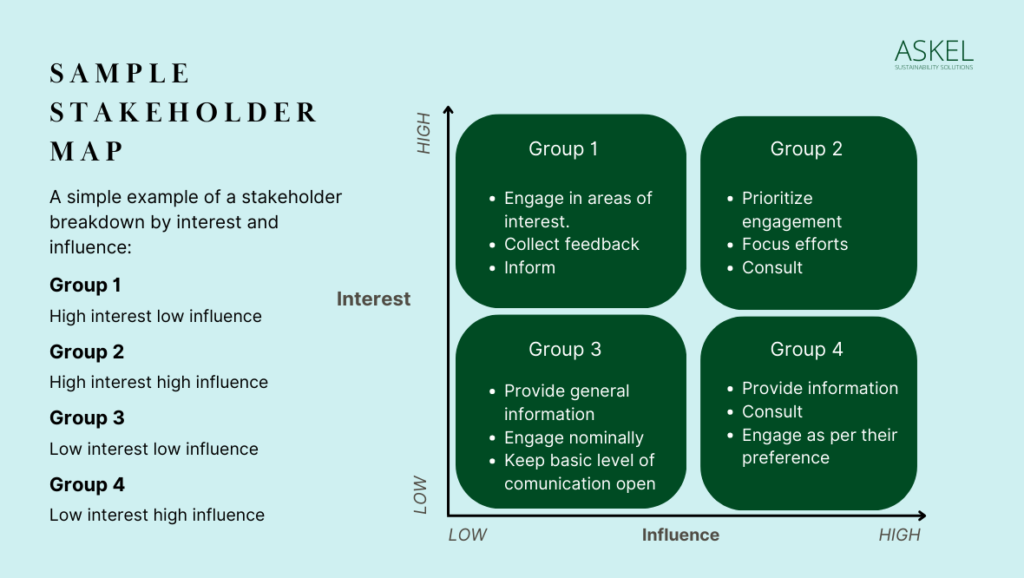
4. Stakeholder Prioritization
Once the stakeholders have been identified, analyzed, and mapped out the organization according to its engagement goals prioritizes them in order of level of engagement. Stakeholders can be divided into sets in order of priority and separate engagement approaches can be decided based on that.
Prioritization can also build on mapping itself where the stakeholder engagement matrix simply divides stakeholders into four sets based on interest and influence and documents engagement needs.
5. Developing a Stakeholder Engagement plan
A stakeholder engagement plan defines in detail how the stakeholder engagement will take place. It is an overarching framework used for the execution of stakeholder engagement.
Key elements of a stakeholder management plan are:
- Action plan
- Communication plan
- Prioritized list of stakeholders
- Stakeholder expectations
Communication plan and strategy
A stakeholder communication plan is a strategy that an organization develops to better communicate, provide information and collect feedback from its stakeholders. A communications plan is central to the effectiveness of the stakeholder engagement process. Additionally, it helps improve relationships with stakeholders and the data quality of feedback received.

6. Sharing Information
Stakeholder Engagement Report
A stakeholder engagement report is an option if an organization has done in-depth engagement and it is a high priority in terms of both the process and its disclosure. The most commonly used standard for stakeholder engagement reporting is the AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard.
Sustainability Report
A more commonly used way of disclosing the efforts and results of stakeholder engagement is sustainability reporting. Reporting standards such as GRI help disclose all pertinent information and are accessible to organizations on various stages of the stakeholder engagement levels.
Website and Social Media
- On a dedicated sustainability page on the organization’s website
- Blog posts
- Social media posts
- Allows for real-time updates as the stakeholder engagement process is carried out
7. Evaluation of stakeholder engagement
Evaluation is necessary in order to determine the success or failure of a stakeholder engagement strategy. There are several tools that an organization can use to evaluate stakeholder engagement.
Evaluation tools:
- Independent external expert evaluation
- KPIs (communication frequency, participation rate, etc)
- Stakeholder engagement matrix based on engagement levels. (unaware, resistant, neutral, supportive, leading)
Today, stakeholder engagement is becoming increasingly prominent in companies, serving as a vital component of internal strategy and transparency. This is because regular proactive engagement fosters trust, facilitates communication, and enables feedback, leading to improved decision-making. Additionally, it plays a pivotal role in establishing trust and goodwill with stakeholders and society at large.


